
Glossary
|
A
Allergen
A protein or cellular component which causes the immune system to mount an allergic reaction to it.
Aflatoxin
A common cancer-producing toxin produced by a fungus called “Aspergillus” which grows on peanuts and grains. Eating mouldy peanuts can result in exposure to this toxin. Drinking the milk and eating the meat of animals which have been fed on mouldy grains are the other common sources of toxin exposure.
Antibiotic-associated diarrhoea
Taking antibiotics can kill the good bacteria residing in our body, besides killing the bad germs which cause illness. Disturbing the normal community of good bacteria in our gut results in symptoms such as diarrhoea, abdominal discomfort and “windiness”. Diarrhoea resulting from taking antibiotics is called antibiotic-associated diarrhoea.
ATCC
ATCC stands for American Type Culture Collection. This is a not-for-profit scientific organisation which collects, analyses, catalogues and stores the genetic information and identification of microorganisms. If a probiotic bacterium has an “ATCC” number it means that the probiotic strain is fully identified and can always be checked, tested and compared with its original strain.
LACTOGG®’s probiotic strain carries the “ATCC 53103” identification number.
Atopic/Allergic March
The Atopic or Allergic March is the term used to describe the typical progression of allergic conditions which begin in infancy to adulthood. This progression usually begins in early infancy as food allergy (eg. cow milk allergy) and move on to allergic skin (atopic dermatitis or eczema), then allergy-associated bronchial asthma and finally nose allergies (allergic rhinitis), later on in life.
It has been postulated that once a child’s immune system is set to “allergic” mode early on in life, it will continue to be allergic for the rest of its life.
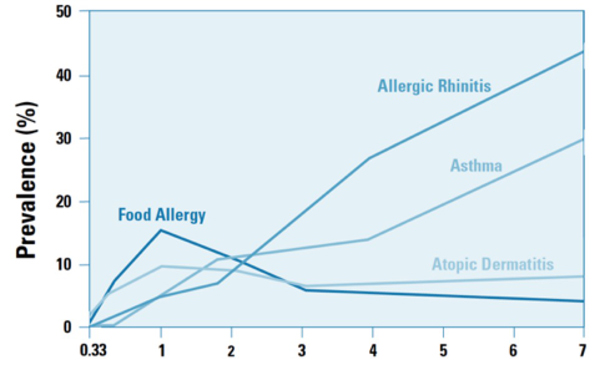
Percentage of children developing the four most common allergic diseases between birth and 7 years old. (Horizontal axis = age in years)[Zieger RS et al., 1989]
Atopy
The allergic response which is defined by symptoms, clinical signs and changes in the immune system.
B
Bacterial culture
A method of multiplying the growth of bacteria in a laboratory. One common type of bacterial culture is the growing of bacteria on special agar plates containing nutrients for the bacteria.
 Growth of Lactobacillus GG on an agar plate.
Bifidobacterium
A genus of bacteria. Many probiotic bacteria belong to this genus. Bifidobacterium bacteria usually cannot survive when exposed to air and oxygen.
Billion
1000 million
Biopsy
A medical procedure where samples of cells or tissue are removed for tests in the laboratory.
C
c.f.u
Acronym for “colony forming units”. It denotes the number of live bacteria present.
Caecum
The first part of the large intestine where fermentation of non-digestible vegetable fibres and carbohydrates by bacteria is most active.
Carcinogen
A substance which causes cancer.
Chemotherapy
A form of cancer treatment, using chemicals and drugs.
Clinical trials
Clinical trials are human studies conducted in a medical facility or by medical doctors and scientists to test if a drug, supplement or treatment is beneficial to humans.
The clinical trial which is most accurate is the randomised, double blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial (RDBPCT). This type of clinical trials tests at least 2 groups of persons, where one group is given the test substance (eg. the probiotic) and the other group is given a dummy substance which looks, smells and tastes the same as the test substance but does not contain any active substance (called the “control”). A computer and not a person determines who gets the test substance and who gets the control (randomised). All the researchers and patients should not know what is being given to whom during the study (called double-blinding) to avoid any bias or cheating.
LACTOGG®’s probiotic strain has over 250 clinical trials documenting its health benefits, making it the most researched probiotic strain available.
Colonisation
Colonisation refers to the process whereby a bacterium attaches to the surface organs, such as the mouth or the gut, and remains on the organ until it is displaced or detached. After LACTOGG®’s probiotic strain colonises the upper respiratory tract, mouth and intestines, it communicates with the surface cells as well as cells of the immune system which produces health benefits.
Commensals
The “good” bacteria which make up our microbiota or bacteria community are called commensals.
Cytokines
Cytokines are proteins which are produced by cells in the immune system when they are triggered or activated. They act as signals for other immune cells to react and respond to harmful substances, germs or irritants.
E
Eczema
Eczema refers to a skin condition which often lasts a long time and is characterised by itchy, dry, scaly, oozy, cracked and thickened skin rash. Eczema is often, but not always, associated with allergy. People who have allergy-related eczema are at increased risk of developing other allergic diseases such as bronchial asthma and allergic rhinitis.
Eczema is often interchangeable with the term “atopic dermatitis”.
G
Gastroenteritis
Gastroenteritis is infection of the gastro-intestinal tract, causing diarrhoea. Other symptoms include vomiting, abdominal pain and fever.
Genus
Genus is a level in the biological classification of organisms which bear similar characteristics.
A simplistic example of how this classification works can be compared to how a person is named. If a person is named Lin Jen Ming (Identity Card No. ABC123), his genus may be called “Lin”, species “Jen” and strain “Ming”. His identification number is “ABC123”.
The genus in probiotic bacteria is usually either “lactobacillus” or “bifidobacterium”.
I
Immune modulation
This refers to modification of the immune response. Modulation can be either stimulation or calming down of the immune response.
LACTOGG®’s probiotic strains have studies which show it can modulate the immune system. Examples of how immune modulation occurs are stimulation of the immune system to produce antibodies and reduction in allergic inflammation when GG probiotic is consumed.
Immune system
The immune system is a system of specialised cells, structures, proteins and molecules which act together to respond to proteins, harmful substances, irritants, infection or invasion by unwelcome germs or cell components.
About 70% of our immune system is located in our gastro-intestinal tract.
Taking LACTOGG®’s probiotic strain has been demonstrated to influence the immune tissues and cells in the gastro-intestinal tract. Any effect in the gut is transmitted to immune cells in the other parts of the body.
Immunity
The ability of the immune system to fight infection or disease.
Inflammation
The response created by the immune system when it is activated by irritants, damaged cells, allergens, harmful substances or microorganisms.
Irritable bowel syndrome
This condition is also known as IBS or “spastic colon”. The cause is unknown but people with this chronic condition suffer from repeated abdominal pain, bloating, “windiness”, diarrhoea or constipation.
Research has shown that IBS patients may have changes in their gut bacteria, immunity and nerve sensitivity.
So far, there is no specific cure for this condition.
L
Lactobacillus
A genus of bacteria. Many probiotic bacteria belong to this genus.
Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG (ATCC 53103)
The most researched and documented probiotic strain in the world. Also known as Lactobacillus GG or GG probiotic.
M
Medical journals
In order for scientific research to be acceptable and trusted, the research papers documenting the scientific data and results of the research must be published. The most trustworthy publications are printed in scientific and medical journals which are known to be of high quality. Such publications should be open to checking, review and criticism by experts in the field before they can be accepted as true.
For example a study which is reported in a commercial lifestyle magazine is far less trustworthy than a clinical trial published in an internationally-renowned medical journal.
LACTOGG®’s probiotic strain has over 1000 scientific research and clinical studies published in internationally-renowned scientific and medical journals such as the British Medical Journal and the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition.
Microbe
A microscopic organism such as a bacterium, fungus, algae or virus. Another term is “microorganism”.
Microbiota
The term refers to the community of “good germs” which lives in our body systems such as the gastro-intestinal tract. This term is usually taken to refer to the good bacteria in the gastro-intestinal tract.
Microflora
Microflora refers to the collection of microscopic organisms (mainly bacteria) which reside in our body systems.
Microorganism
A microorganism is a microscopic organism such as a bacterium, fungus, algae or virus. Another term is “microbe”.
N
Nosocomial
A nosocomial infection is one which is acquired in a hospital.
P
Pathogen
A harmful or “bad” germ.
Placebo
In a good clinical trial, in order to test if a substance or treatment (eg. taking probiotic) works or not, one group of patients or human subjects is given the test substance and the other group is given a dummy substance called the “placebo”.
This dummy substance looks, smells and tastes the same as the test substance but does not contain the test substance. It s used as a “control” for the clinical study.
Prebiotics
Prebiotics are indigestible food ingredients, usually vegetable fibre and carbohydrates which can be fermented by bacteria in the intestinal tract. Prebiotics support the growth as well as stimulate the activity of good bacteria enabling them to produce health-promoting effects.
The prebiotic contained in LACTOGGВ®+ is called fructooligosaccharide.
Probiotic
A probiotic is a specific strain of live microorganisms which, when consumed in high enough numbers, produce a health effect on the person or animal taking it.
R
Radiotherapy
Radiotherapy is a term describing the form of treatment of cancer using radiation.
S
SCFA
SCFA is the acronym for short chain fatty acids. These substances are produced when non-digestible dietary fibre is fermented by gut bacteria. The main portion of the intestine in which this fermentation process occurs is the first part of the large intestine called the caecum. SCFA provide nutrition to the intestinal cells. They also affect many bodily functions such as blood sugar control and cholesterol regulation.
Scientific publication
A scientific publication is a report of the findings of scientific research which is published. The most trustworthy publications are printed in well-known, high quality scientific and medical journals. Such publications should be open to checking, review and criticism by experts in the field before they can be accepted as true.
LACTOGG®’s probiotic strain has over 1000 scientific research and clinical studies published in internationally-renowned scientific and medical journals.
Species
Species is a level in the biological classification of organisms which bear similar characteristics.
A simplistic example of how this classification works can be compared to how a person is named. If a person is named Lin Jen Ming (Identity Card No. ABC123), his genus may be called “Lin”, species “Jen” and strain “Ming”. His identification number is “ABC123”.
The species in probiotic bacteria is usually the second word in its name. Eg. The species identity in the probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG (ATCC 53103) is “rhamnosus”.
Strain
Strain is a level in the biological classification of organisms which bear similar characteristics.
A simplistic example of how this classification works can be compared to how a person is named. If a person is named Lin Jen Ming (Identity Card No. ABC123), his genus may be called “Lin”, species “Jen” and strain “Ming”. His identification number is “ABC123”.
The strain in probiotic bacteria is usually the last word/letters in its name. Eg. The strain identity in the probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG (ATCC 53103) is “GG”.
If a bacterium only has a genus and species name and does not have a strain identity (eg. Lactobacillus acidophilus) it is impossible to confirm if it has health benefits or not, because every probiotic strain confers different health benefits. Otherwise it cannot be classified as a true probiotic.
Symbionts
Symbionts are the biological components of a symbiosis. For example, man and bacteria are symbionts.
Symbiosis
Symbiosis refers to the biological interaction between two or more different species which is mutually beneficial. Bacteria have over time evolved to live in symbiosis, on and in our bodies. These “good” bacteria are an essential component in human function and health.
Synbiotic
A synbiotic is a mixture containing a probiotic and prebiotics. LACTOGGВ®+ sachets contain the GG probiotic and enough fructooligosaccharide to qualify as a true synbiotic.
T
Th1 immune profile
Our immune system is meant to protect us from infections and harmful substances. This is usually achieved by immune signals and cells called the Th1 cells. Usually our Th1 cells are active and our immune responses take on Th1 characteristics.
Th2 immune profile
Activity and immune signals involving Th2 immune cells produce allergic inflammation. If a baby continues to have more Th2 responses instead of Th1 activity the child will become allergic.
Traveller’s diarrhoea
When a person travels to another place or country he or she is exposed to new and unusual germs, making the traveller susceptible to diarrhoea and vomiting. It has been estimated that about 50% of travellers suffer from some form of traveller’s diarrhoea. The most common germ which causes traveller’s diarrhoea is called enterotoxigenic E. coli or ETEC.
Treg cells
Treg cells are T-regulatory cells. They are a type of immune cells which suppresses the immune system’s response so that it does not over-react. They are responsible for shutting down the immune responses after they have done their job of eliminating bad germs or eradicating harmful molecules, protecting our body from being harmed by too much immune activity or inflammation. These cells have been called the “self-check” or “balancer” immune cells.
LACTOGG®’s probiotic strain has studies showing that it can influence our immune system by increasing T-reg cell activity.
Y
Yoghurt starter
A yoghurt starter is a bacterium which is used to turn milk into yoghurt. Two of the most common yoghurt starters are Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Stretococcus thermophilus. A yoghurt starters are not probiotics because they cannot survive to colonise the intestinal tract. Without colonisation, they cannot give probiotic health benefits to the person. Some probiotic products include yoghurt starters to claim they have a large number of bacteria although they do not have any probiotic health benefits.
|