Gastroenteritis is a very contagious condition. It can spread rapidly within families, playgroups and nurseries.
Clinical studies have shown that consuming GG probiotic regularly can reduce the incidence of gastroenteritis in babies and children.
GG probiotic given to babies and young infants reduced their risk of contracting diarrhoea by almost 80%.
Lactobacillus GG reduces the risk of developing diarrhoea. [Szajewska et al. 2001]
In another study, children living in unhygienic conditions were given GG probiotic in jelly, over 15 months. The researchers found that breastfeeding protected the children from developing acute gastroenteritis. Of those toddlers who were not breastfed, GG probiotic reduced the occurrence of acute diarrhoea throughout the study period.
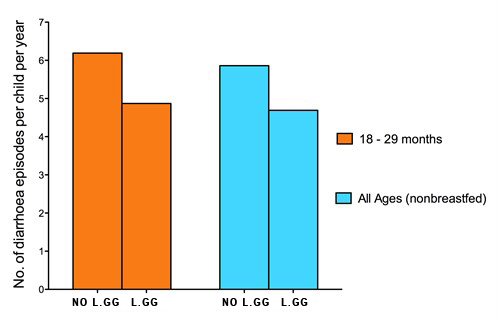 Incidence of diarrhoea in children not receiving breastfeeds. [Oberhelman et al. 1999]
Incidence of diarrhoea in children not receiving breastfeeds. [Oberhelman et al. 1999]
References:
Hojsak I et al.Lactobacillus GG in the prevention of nosocomial gastrointestinal and respiratory tract infections. Pediatrics 2010;125(5):e1171-1177
Kaila M et al.Enhancement of the circulating antibody secreting cell response in human diarrhea by a human lactobacillus strain.Pediatr Res 1992;32(2):141-144
Oberhelman RA et al. A placebo-controlled trial of Lactobacillus GG to prevent diarrhea in undernourished Peruvian children. J Pediatr 1999;134:15-20
Pant N et al. Effective prophylaxis against rotavirus diarrhea using a combination of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG and antibodies. BMC Microbiol 2007;7:86
Szajewska H et al.Efficacy of Lactobacillus GG in prevention of nosocomial diarrhea in infants.J Pediatr 2001;138(3):361-365