|
Clinical trials have documented that consuming GG probiotic reduces the risk of women putting on excessive weight after childbirth. It also protects children from becoming overweight.  The possibility of weight gain after pregnancy is of great concern to every woman. A clinical study noted that women who consumed a probiotic preparation containing GG probiotic during pregnancy and breast feeding were less likely to develop a big waistline 6 months after childbirth. The women in the probiotic group also had the lowest upper arm thickness, 1 year after childbirth. 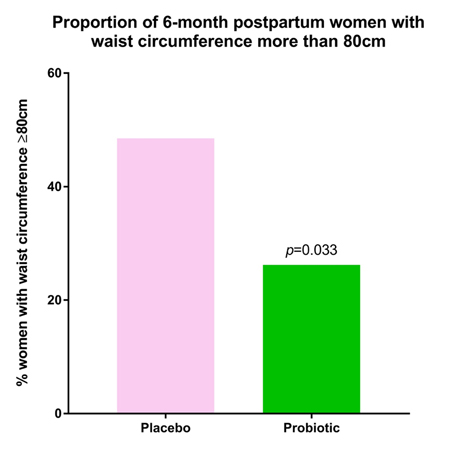
Proportion of women with waist circumference of > 80 cm at 6 months after delivery. [Ilmonen et. al. 2011]
In a long term study, the growth of over 100 children who were exposed to GG probiotic in early infancy was monitored until they were 10 years old. A measure of the children’s weight called the Body Mass Index (BMI) was calculated. The paediatricians found that in the group of children who became obese at 10 years old, those who took GG probiotic hen they were babies had a lower BMI at every measurement compared to those who were not exposed. Moreover, the children in the probiotic group did not gain excessive weight before they were 4 years old. 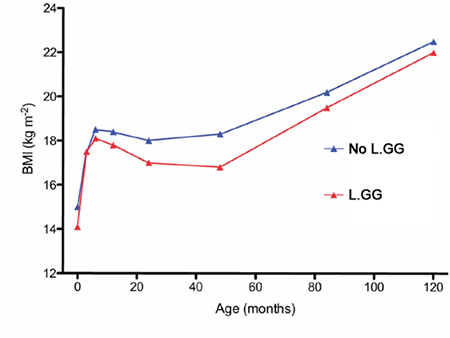
BMI of children followed up from birth to 10 years of age. [Luoto et al. 2010]
This 10 year study demonstrates that colonisation with LACTOGG®’s probiotic strain during infancy restrains the child from gaining excessive weight in the first few years of life. References: Ilmonen J et al. Impact of dietary counselling and probiotic intervention on maternal anthropometric measurements during and after pregnancy: A randomized placebo-controlled trial. Clin Nutr 2011;30(2):156-164 Luoto R et al. The impact of perinatal probiotic intervention on the development of overweight and obesity: follow-up study from birth to 10 years. Int J Obes (2010) 34, 1531–1537 |




